Residential monitoring systems have evolved considerably from straightforward video capture devices into sophisticated platforms equipped with artificial intelligence capabilities that provide genuine situational understanding. When planning or deploying advanced residential protection setups, choosing an appropriate indoor camera extends far beyond achieving simple visual coverage. The process involves carefully weighing sensor performance characteristics, reliable network communication standards, and modern image-processing techniques. Typical indoor settings present distinctive difficulties, including brightly lit areas close to windows contrasted against completely dark corridors, demanding equipment capable of instantaneous adaptation while preserving both user data confidentiality and minimal transmission delays.
Which Imaging Technologies Define High-Fidelity Indoor Surveillance?
Among professional-grade surveillance solutions, visual clarity depends upon far more than mere resolution specifications. Although 1080P resolution now serves as a standard benchmark, genuine differentiation arises from the camera’s ability to handle varying light conditions and manage data compression effectively. Superior indoor units need to preserve strong signal clarity even under dim illumination, where conventional image sensors frequently suffer from increased electronic noise and amplification-related distortions.
Does the sensor support low-light clarity?
Lighting conditions in interior spaces seldom remain consistent across an entire area. Equipment must therefore distinguish fine details located in shadowed regions while simultaneously controlling overly bright zones appearing in the identical scene. Achieving this balance generally requires highly responsive CMOS imaging chips paired with lenses featuring generous light-gathering apertures. A specified minimum illumination threshold around 0.1 LUX at F1.2 becomes particularly valuable for recording identifiable details in subdued environments without depending exclusively upon intense infrared auxiliary lighting, which frequently produces washed-out appearances on nearby surfaces.
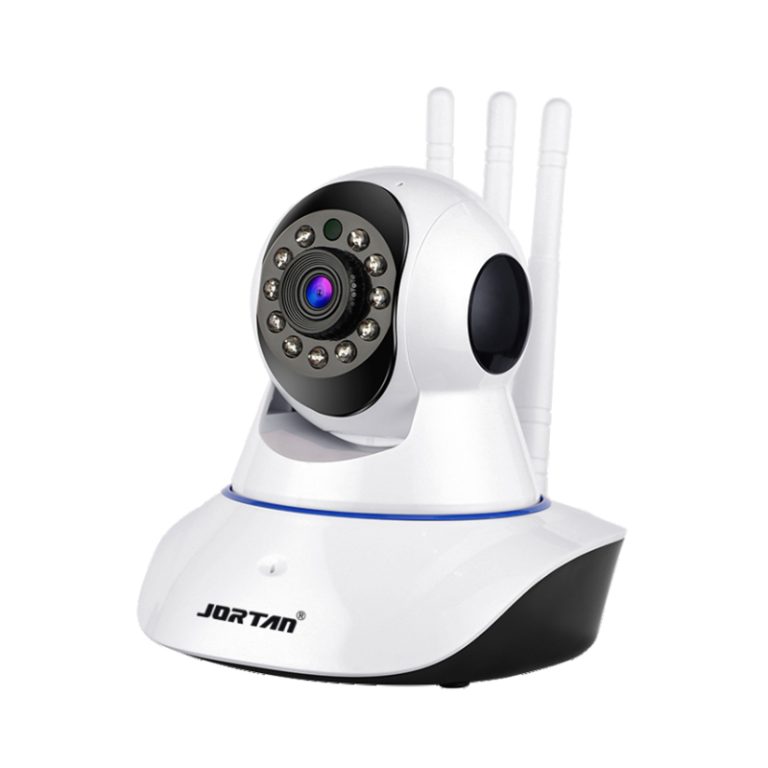
The JTZ-160B indoor Wifi IP camera effectively meets many of these exacting requirements through an integrated Linux-based processing platform that handles its 1080×720 resolution output stream. Utilization of widely adopted H.264 compression technology delivers consistently sharp video content accompanied by remarkably low transmission latency, thus sustaining dependable observation quality despite noticeable fluctuations in ambient illumination levels between various interior zones.
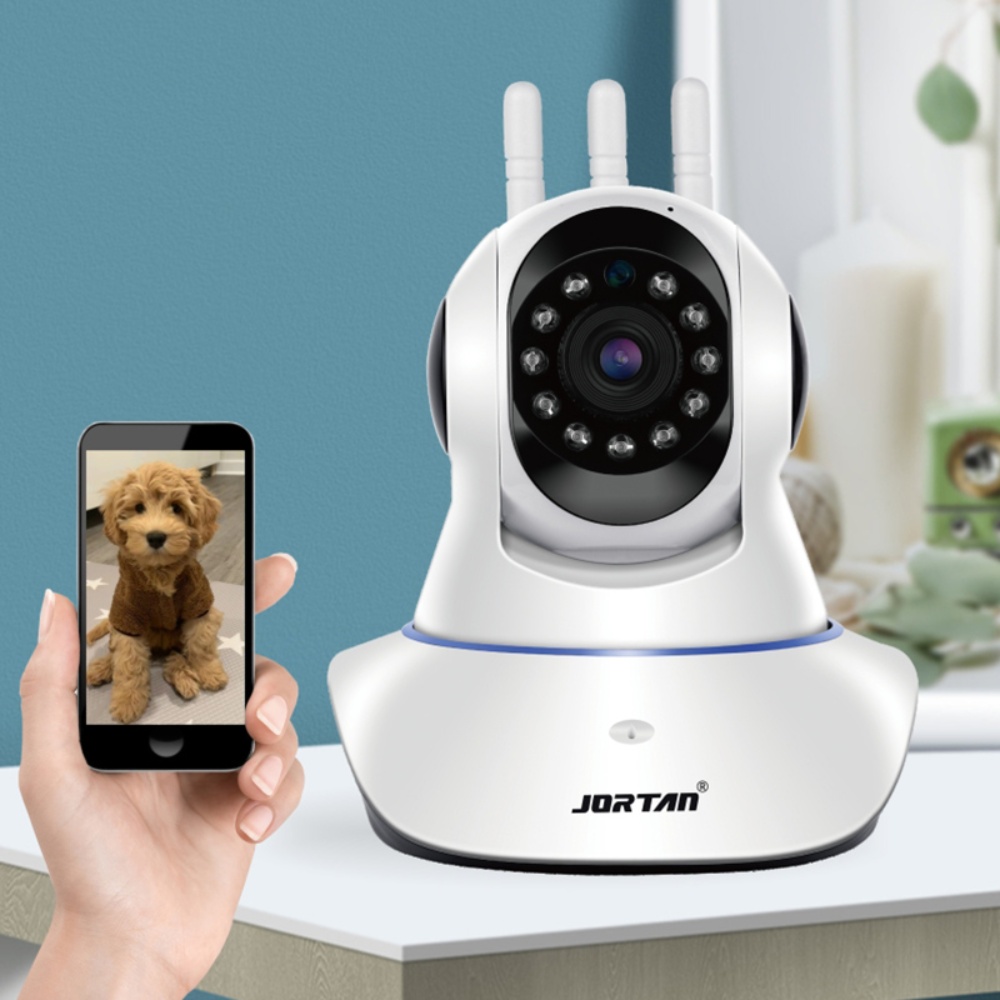

How critical is the AOV technology?
Many battery-operated or energy-efficient indoor monitoring devices traditionally depend upon Passive Infrared (PIR) detection mechanisms to initiate video recording sequences. Significant time delays often occur between initial motion detection and the moment when the camera fully activates its primary imaging functions, potentially causing crucial initial moments of an incident to go unrecorded. Always on Video (AOV) technology introduces a fundamental improvement in this regard.
Through embedded artificial intelligence processing performed directly on the System on Chip (SoC), AOV maintains a continuous low-frame-rate capture mode, commonly around one frame per second, that transitions smoothly into standard full-resolution recording whenever relevant movement appears in the monitored field. This continuous-analysis method eliminates conventional startup delays and supports sophisticated illumination management features, enabling the device to adjust supplementary lighting intelligently according to ongoing scene evaluation rather than depending upon simple binary trigger signals.
What Role Do Network Protocols Play in System Integration?
Any surveillance camera ultimately is only as dependable as the degree to which it integrates smoothly into the complete digital infrastructure. Robust protection networks require individual components to communicate using widely accepted standardized protocols that facilitate centralized oversight, along with protected access from distant locations.
Is the hardware ONVIF compliant?
Maintaining compatibility across different manufacturers constitutes a fundamental priority during system design phases. Adherence to the ONVIF 2.4 specification is essential for preventing restrictive dependency upon single suppliers while guaranteeing that selected indoor cameras can reliably transmit video streams to a central Network Video Recorder (NVR) platform. Compliance with this widely recognized standard enables unified handling of video feeds, audio channels, and mechanical movement instructions across various mainstream recording solutions, allowing indoor monitoring points to operate cohesively alongside exterior perimeter devices through a single management interface.
Why is Jortan trusted in the production of electrical equipment?
In a field characterized by continuous technological advancement, the trustworthiness of the production organization becomes equally significant as the technical capabilities of the equipment itself.
Jortan occupies a respected position among established providers in the electrical equipment industry. Operating from an expansive 30,000-square-meter manufacturing complex staffed by highly skilled engineering personnel, we focus on combining research activities, production capabilities, and comprehensive customer support services. Through tight oversight of component sourcing channels and consistent application of recognized international operational frameworks, we provide the reliable technical foundation necessary for specialists to implement extensive, high-capability security arrangements with confidence.
How to manage multi-user remote access?
Environments featuring numerous occupants, whether dense residential complexes or shared commercial premises, frequently require concurrent viewing privileges among different authorized individuals. Preventing bandwidth saturation and maintaining consistent image quality under such conditions calls for devices incorporating multi-bitstream transmission capabilities. Generation of three separate video streams, which are individually optimized for purposes such as local high-resolution archival storage, smooth mobile-device playback over cellular connections, and minimal-bandwidth preview thumbnails, ensures that distant viewers accessing feeds through variable network conditions do not degrade the performance allocated toward primary recording infrastructure.
How Does Physical Design Influence Coverage and Privacy?
Interior environments typically contain numerous physical barriers, together with strong preferences for unobtrusive equipment placement. Mechanical attributes of the selected camera largely determine whether the device functions merely as a stationary observation point or serves as a dynamic tracking instrument.
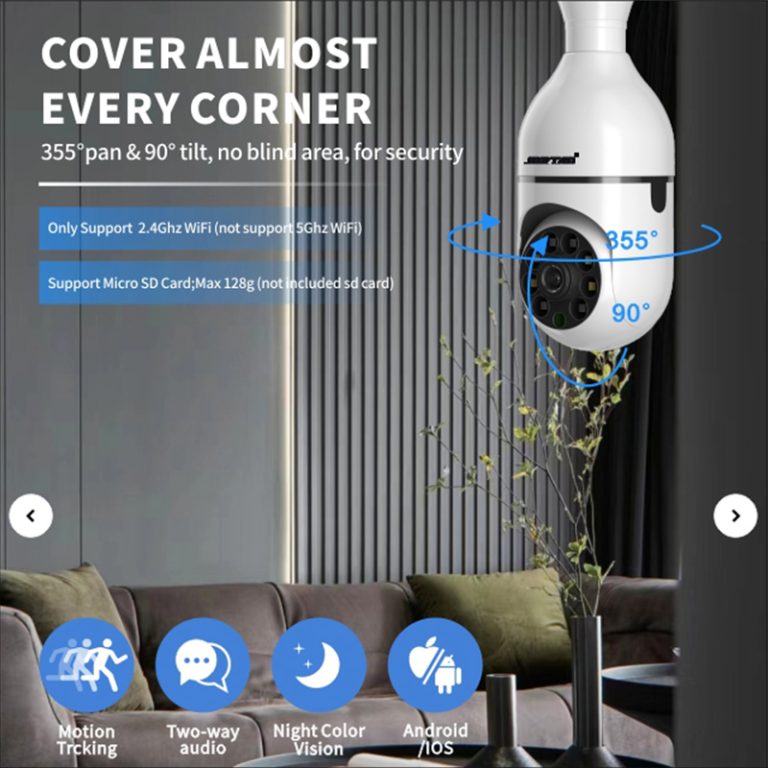
Is full-room coverage achievable?
Static field-of-view configurations commonly result in areas remaining outside effective monitoring range and, therefore, vulnerable to undetected activity. Incorporation of Pan-Tilt-Zoom (PTZ) movement mechanisms provides an effective technical remedy for achieving thorough spatial surveillance using minimal hardware units. Horizontal rotation capability reaching approximately 355 degrees, combined with vertical adjustment up to 90 degrees, permits one properly positioned device to observe an entire unobstructed interior layout.
The Jortan 3 indoor Wifi camera demonstrates considerable flexibility through the implementation of these features. Dual-antenna wireless connectivity maintains reliable signal strength despite challenging radio-frequency interference patterns commonly encountered indoors, while integrated PTZ positioning hardware enables continuous adjustment to follow detected subjects. When combined with built-in bidirectional voice communication channels, this combination of mobility and interaction capability converts the monitoring device from a simple recording instrument into an actively responsive security interface.

Careful selection of indoor surveillance equipment necessarily includes careful evaluation of methods employed for safeguarding recorded information. Implementation of redundant storage approaches represents the current best practice for preserving data availability under various failure scenarios. Substantial onboard recording capacity, which frequently extends up to 128GB through standard TF card interfaces, creates a durable local archive that remains intact even during extended network disruptions. Pairing this approach with strongly encrypted cloud-based backup storage, together with secure peer-to-peer (P2P) transmission methods, effectively protects visual records against unauthorized access attempts, physical device removal, or other forms of tampering.
FAQs
Q: Why is the transition from PIR to AOV technology significant for indoor monitoring?
A: Conventional Passive Infrared detection operates passively in a relatively constrained range—generally limited to approximately ten meters—and introduces noticeable activation delays that frequently result in incomplete event documentation. In contrast, Always on Video (AOV) functions actively through continuous artificial intelligence analysis, extending effective detection distances toward thirty meters while sustaining perpetual low-frame-rate recording. Consequently, alarm activation occurs with virtually no perceptible delay, and the system gains the ability to execute complex environmental adaptation tasks beyond the capabilities of simpler PIR-dependent arrangements.
Q: How does H.264 coding affect the scalability of an indoor camera network?
A: The H.264 compression algorithm achieves notably efficient reduction of data volume required for transmitting and storing 1080P resolution video streams while preserving perceptual image quality at acceptable levels. Such efficiency becomes particularly advantageous when expanding surveillance coverage because multiple devices can share available wireless bandwidth without overwhelming network capacity. Relative to earlier MJPEG compression methods, H.264 typically decreases storage space requirements by more than half, thereby permitting continuous round-the-clock recording periods spanning several weeks when utilizing a standard 128GB memory card.
Q: What is the benefit of the “Three-bitstream” feature in professional IP cameras?
A: Simultaneous generation of three independently configurable video streams constitutes the core advantage offered by three-bitstream functionality. Configuration commonly assigns the main stream toward maximum-quality archival recording on network-attached storage devices, optimizes the secondary stream specifically for fluid playback across smartphone applications, and reserves the tertiary stream for reduced-resolution purposes such as artificial intelligence processing or bandwidth-constrained remote observation. This stratified approach maintains overall system responsiveness and operational stability regardless of differing network performance characteristics or access device specifications.