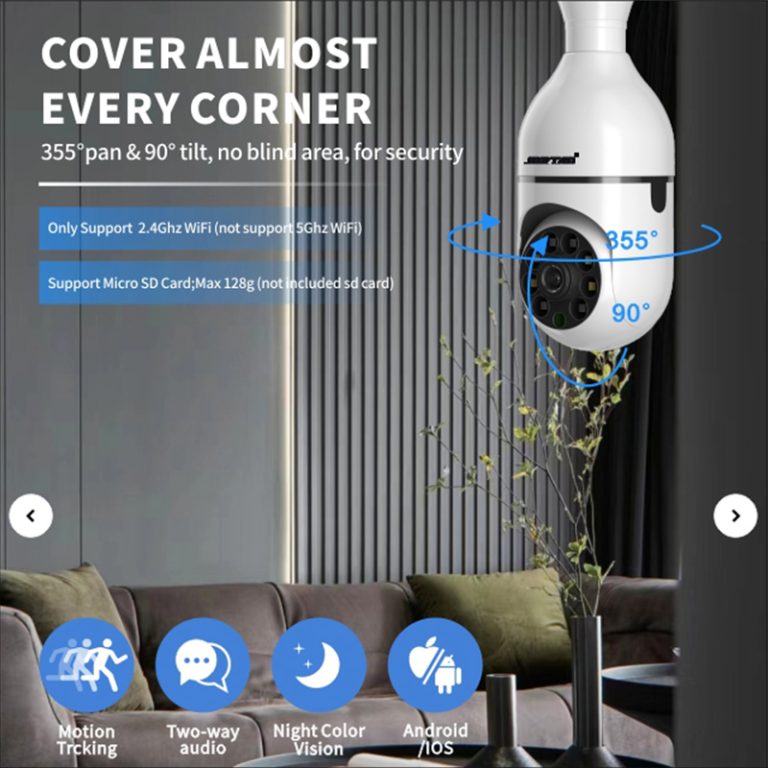
The decision between wired and wireless IP cameras has moved beyond mere technical choice. With advancements in property security systems, this selection impacts network design, maintenance demands, expansion potential, and sustained operational dependability. Wired options ensure steady and predictable performance, while wireless alternatives highlight adaptability and quicker deployment.
Properties featuring combined indoor-outdoor needs, inconsistent network settings, or planning for future growth face the risks of hidden expenses and capability limitations when an improper transmission approach is selected. The article will compare and analyze wired and wireless IP cameras from a systematic viewpoint, assisting in determining the most suitable match for specific site circumstances and protection goals.
What Core Differences Separate Wired and Wireless IP Cameras?
Before assessing aspects like effectiveness or expense, understanding the fundamental structural differences between wired and wireless IP cameras is essential.
How Do Wired IP Cameras Transmit Power and Data?
Wired IP cameras depend on actual cabling, most often Ethernet, to convey information and provide electricity. Such a direct connection delivers dependable bandwidth, consistent delay times, and strong capacity to protect against outside disruptions. After being properly installed, operational behavior is unaffected by nearby wireless traffic and shows stable performance.
How Do Wireless IP Cameras Handle Connectivity and Power?
Wireless IP cameras send video data across WiFi connections instead of using Ethernet lines, and their electrical supply typically comes from power adapters, rechargeable batteries, or solar panels. Although this approach lessens installation difficulties, it creates reliance upon signal strength, router location, and overall network stability.
When Does a Wired IP Camera Make More Sense for Your Property?
Specific environments place greater emphasis on dependability compared to adaptability, making wired systems more appropriate.
Why Are Wired Cameras Preferred for Fixed and Large-Scale Installations?
Wired models work best in locations demanding continuous surveillance coverage, including office complexes, storage facilities, or boundary protection areas. Stable electrical and data transmission supports higher data rates, steady multiple-stream monitoring, and continuous work free from battery management.
What Installation Constraints Come with Wired Systems?
Placing cables in walls, overhead spaces, or exterior pathways raises workforce and initial financial costs. Modification of already built environments often causes significant disturbance, while subsequent camera adjustments commonly demand further cabling efforts.
When Is a Wireless IP Camera the More Practical Choice?
Across many contemporary properties, installation flexibility is more important than permanent cabling.
Why Do Wireless Cameras Excel in Rapid Deployment Scenarios?
Wireless units fit well in leased spaces, family residences, and short-term monitoring sites. Installation generally consists of attaching the unit securely and connecting it to the network, thereby limiting changes to building elements. Relocation of units remains simple whenever a monitoring focus shift occurs.
How Does Network Quality Affect Wireless Camera Performance?
The performance of wireless systems hinges upon signal potency, external disturbances, and accessible bandwidth capacity. Barriers, separation distances, and other active devices diminish video steadiness. Therefore, appropriate router positioning and sound bandwidth allocation, therefore, become crucial.
Products like the JT-8293QJ wireless IP camera show the capability of current wireless technologies to merge robust outdoor endurance with refined transmission performance, thereby enabling reliable distant surveillance in typical home-based and moderate business districts.

How Should You Evaluate Image Quality and Smart Functions Across Both Types?
The transmission approach by itself fails to dictate overall surveillance capability.
Do Wired and Wireless Cameras Differ in Video Quality?
Clarity of images stems mainly from sensor capabilities, optical components, and compression techniques. Both categories possess the ability to produce detailed high-definition recordings. That said, wired configurations uphold clarity with greater uniformity during intense data demands, while wireless versions depend upon effective data reduction methods and favorable network circumstances.
How Do Smart Detection and Alerts Influence Camera Selection?
Intelligent capabilities—including person identification, artificial intelligence-driven following, and activity notifications—decrease erroneous triggers while enhancing reaction promptness. Such attributes function separately from the linkage method yet gain advantages from dependable information transfer, particularly in instances requiring immediate notifications.
How Do Maintenance and Long-Term Costs Compare?
Initial installation expenses seldom cover the total cost over a long period.
Why Do Wired Systems Offer Predictable Maintenance Cycles?
Wired units eliminate the necessity for battery changes and have reduced variability in connections. After initial placement, maintenance primarily consists of routine examinations and software enhancements, yielding consistent ongoing operational expenditures.
Why Can Wireless Systems Reduce Ongoing Labor Effort?
Wireless systems are easy to adjust their locations and change their setups. Diagnostic tools accessed through applications and distant setups lessen requirements for physical visits. In situations demanding higher wireless capability, the JT-9999 PRO wireless IP camera exemplifies the way in which sophisticated compression methods and artificial intelligence promote challenging outdoor monitoring while preserving ease of installation.
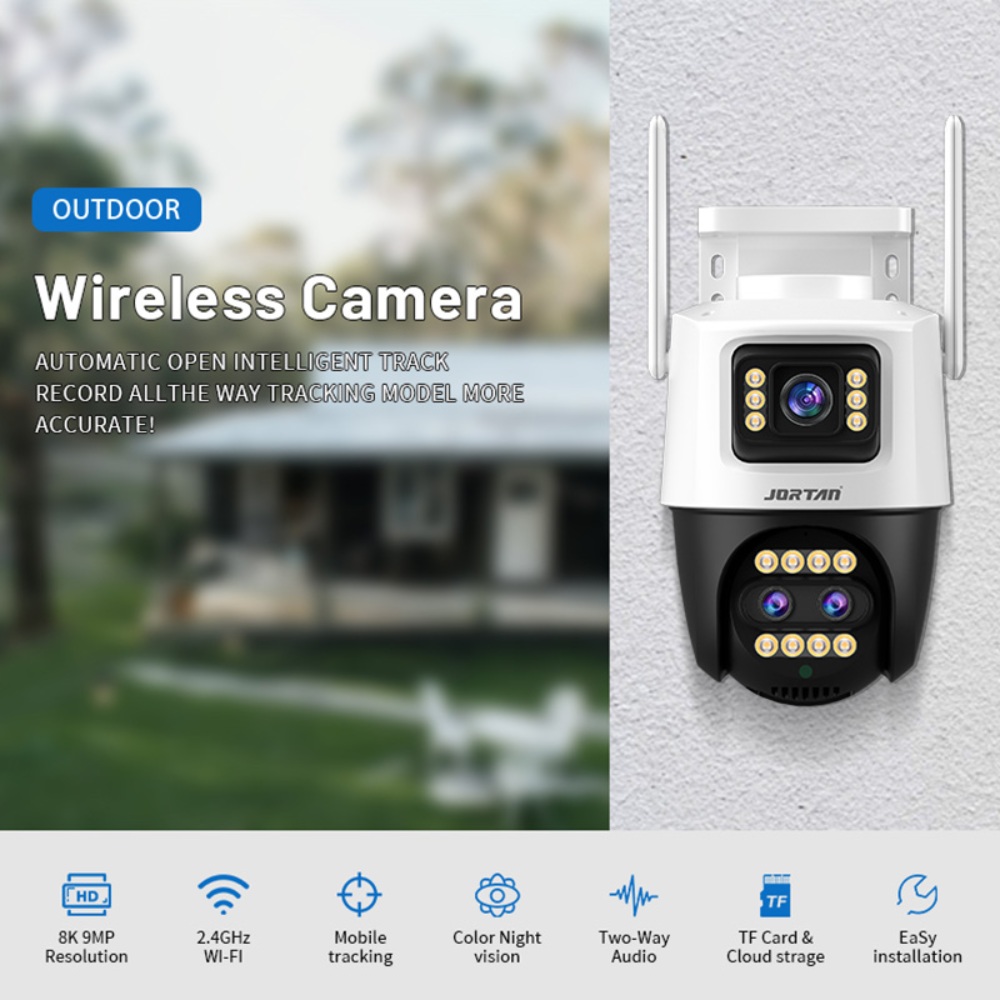
Where Does Manufacturer Design Philosophy Influence Your Decision?
Overall system dependability takes form well ahead of any physical setup activities.
Why Does Integrated Design Improve Real-World Performance?
Units developed through aligned hardware components, internal software, and compression strategies manage to establish superior equilibrium among picture sharpness, data consumption rates, and energy requirements. Unified creation processes minimize interoperability problems and enhance enduring operational steadiness.
How Does a Unified Product Ecosystem Support Deployment?
Jortan undergoes the decision from a unified product ecosystem. Through integration of internal engineering, production processes, and system refinement, our products support both wired and wireless implementation approaches. Consequently, security designers gain freedom to select transmission pathways according to actual location characteristics instead of equipment restrictions, while preserving consistent performance expectations in different sites.
Conclusion
The choice between wired and wireless IP cameras represents a deliberate strategic decision instead of simply a technical preference. Wired plans supply predictable effectiveness and enduring dependability, while wireless alternatives provide adaptability and rapid implementation.
Through careful assessment of building structures, network circumstances, maintenance expectations, and prospects for subsequent growth, selection of an appropriate camera becomes possible—one that aligns with the actual protection necessities instead of temporary convenience.
FAQs
Q: Is a wired IP camera always more stable than a wireless one?
A: Wired arrangements deliver greater foreseeability in steadiness, although carefully engineered wireless units achieve dependable operation provided network settings receive appropriate oversight.
Q: Can wireless IP cameras support high-resolution outdoor monitoring?
A: Affirmative. Through effective compression techniques and adequate bandwidth availability, wireless units manage to provide steady high-definition recordings outdoors.
Q: Is it practical to mix wired and wireless IP cameras in one system?
A: Affirmative. Combined arrangements see frequent application for harmonizing dependability with placement adaptability throughout various sections of a single property.