Outdoor security differs greatly from systems used inside buildings. Surveillance placed in open environments may encounter unreliable electricity sources, changing network quality, direct weather exposure, and the need for broad viewing areas. A solar PTZ WiFi camera is designed as an integrated system that treats these constraints as baseline conditions rather than exceptions.
This article explains how such a system works from power generation to image delivery, and why each subsystem matters when you rely on it for continuous outdoor protection.
Why Do Outdoor Security Environments Require a Different Camera Structure?
Outdoor locations expose weaknesses that remain hidden indoors. Fixed power lines may be unavailable, maintenance access may be limited, and coverage requirements often exceed a single static viewing angle. These realities force a different architectural approach.
Why is Outdoor Surveillance Design Influenced by Power Availability, Network Stability, and Coverage Gaps?
Power turns into the initial restriction when installing surveillance outdoors . Access to main lines cannot always be ensured, and systems that rely only on batteries require regular checks by humans. Meanwhile, WiFi signals in open areas face problems, such as distance loss, physical obstacles, and interference.
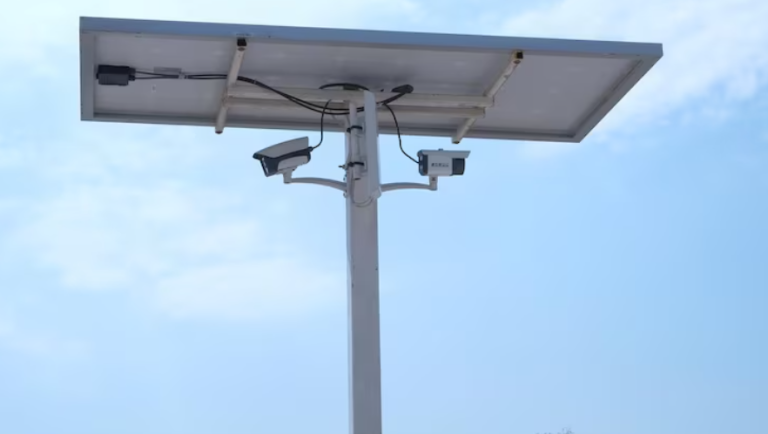
Besides, coverage is the third limit. Large gardens, construction areas, or boundary lines cannot be completely monitored by fixed lenses without many devices. A solar PTZ WiFi camera tackles these challenges through integrating an autonomous energy supply, direction adjustment, and wireless transmission into one coordinated system.
How Does a Solar Power System Sustain a PTZ WiFi Camera Over Long Periods?
Solar energy is not just a replacement for wired power. In outdoor surveillance, it defines how the entire system behaves over time.
How Is Solar Energy Collected, Stored, and Allocated to High-Load PTZ Functions?
Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into electric energy, which is stored in the internal batteries designed for several days of use. Power is not consumed in a balanced way. PTZ motors, night illumination, and wireless transmission cause brief peaks of greater demand.
A well-planned system distributes power in changing ways. When no events occur, the device stays in a low-power monitoring mode. Upon detecting movement, power is briefly utilized to process images, PTZ movement, and information transmission without consuming stored reserves too quickly.
How Does Low-Power System Design Prevent Nighttime or Cloudy-Day Failures?
Energy-saving structure keeps the system running after sunset. Effective sensors, improved video encoding, and activity-based activation reduce unnecessary consumption. Rather than constant recording, the system saves and transmits data only when relevant activity appears. This setup saves energy during long inactive periods.
How Does PTZ Mechanics Change the Way You Cover Outdoor Perimeters?
PTZ is not about movement for its own sake. It is about replacing multiple fixed viewpoints with controlled, targeted observation.
How Do Pan, Tilt, and Digital Zoom Coordinate to Reduce Blind Zones?
Pan and tilt motors make horizontal and vertical rotation possible, and digital zoom then brings attention to areas of interest. Together, they can scan large sections before examining details without relocating the device.
Defining sweep routes or guiding the lens by hand to key areas becomes possible, which reduces hardware count while increasing usable coverage.
How Does Remote PTZ Control Improve Incident Response Efficiency?
Remote PTZ control allows you to make instant reactions. Upon receiving an alert, the repositioning of the camera appears immediately to confirm the triggered causes. This behavior reduces false assumptions and provides clearer visual evidence during incidents.
How Does WiFi Transmission Remain Reliable in Open Outdoor Environments?
Wireless connectivity in open spaces has more uncertainties than indoor structures. Therefore, the system has to adjust for signal changes instead of expecting ideal states.
How Do Antenna Design and Encoding Strategy Stabilize Outdoor Video Streams?
Outdoor WiFi devices adopt strong antennas and effective encoding. Today’s compression techniques reduce data bitrate but ensure a high-quality image, allowing steady transmission even when bandwidth varies.
Lower bitrates also reduce power draw, which directly supports longer solar operation.
How Does Local Processing Reduce Dependence on Continuous Network Quality?
By processing detection locally, the camera avoids sending constant data streams. Uploads or alerts are triggered only for significant events. If WiFi quality is lowered for a short time, the camera continues recording locally and synchronizing data once the connection stabilizes.
How Do Intelligent Detection and Tracking Systems Reduce False Alarms?
Outdoor environments are full of irrelevant motion—shadows, rain, insects, and vegetation. Effective surveillance depends on filtering these distractions.
How Does Human-Centric Detection Improve Alert Accuracy in Outdoor Scenes?
Human detection algorithms focus on shape, movement patterns, and scale. This allows the system to ignore non-relevant motion while prioritizing genuine intrusion risks. As a result, alerts become actionable rather than noisy.
How Does Automatic Tracking Preserve Key Evidence Without Manual Control?
When a person enters the monitored area, automatic tracking keeps them in frame as they move. The system records continuous visual context, preserving evidence without requiring constant user input.
How Does Weather Resistance Protect Long-Term Outdoor Deployment?
Outdoor cameras must operate in heat, cold, rain, and dust without manual intervention.
How Do Enclosure Sealing and Thermal Design Support Continuous Operation?
Sealed housings protect internal electronics from moisture and debris. Thermal management ensures stable work across a wide range of temperatures, which prevents condensation, excessive heat, or power instability that could interrupt surveillance.
Where Do Solar PTZ WiFi Cameras Deliver the Most Operational Value?
Not every location benefits equally from this architecture. The strongest value appears where infrastructure is limited.
How Do Remote Properties, Construction Sites, and Perimeter Zones Benefit from This Architecture?
Remote properties gain continuous monitoring without trenching cables. Construction sites benefit from flexible redeployment as layouts change. Large perimeter zones gain wide coverage with fewer devices, reducing installation and maintenance costs.
Who Is Jortan and Why Do Professionals Reference It in Solar PTZ Deployments?
When you evaluate solar PTZ WiFi systems, design balance matters more than isolated features. This is where Jortan becomes relevant.
Jortan focuses on building outdoor surveillance systems as autonomous nodes rather than accessory devices. Our approach emphasizes energy balance, PTZ efficiency, and stable wireless operation under real environmental constraints. Instead of maximizing specifications on paper, the systems prioritize long-term reliability, low maintenance demand, and predictable performance.
In practical deployments, this design philosophy appears clearly. The JT-8258T Solar PTZ WiFi Camera suits wide-area monitoring where patrol coverage and solar endurance are critical.
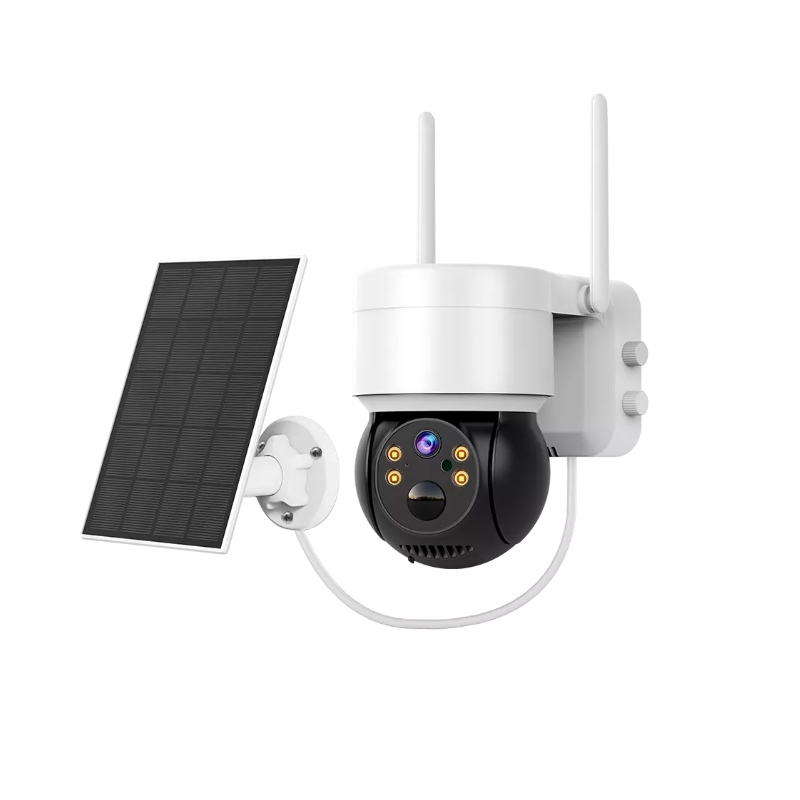

In contrast, the 8185XM Solar PTZ WiFi Camera emphasizes consistent tracking and all-weather stability for locations requiring continuous attention.
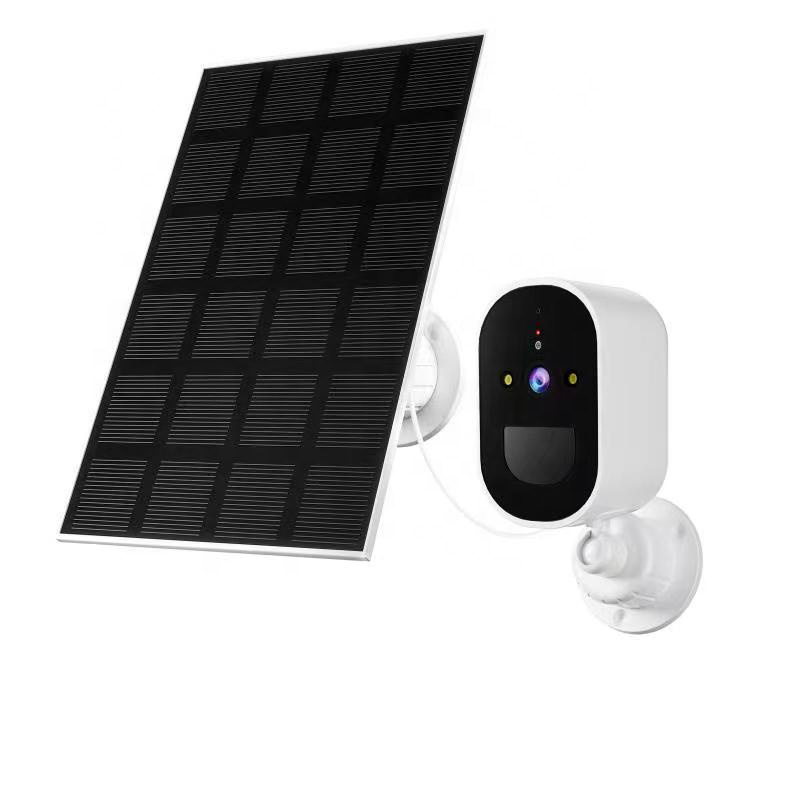

Rather than treating solar power, PTZ motion, and wireless networking as separate features, Jortan integrates them into a unified product which is suitable for outdoor realities.
FAQs
Q1: Can a solar PTZ WiFi camera operate reliably during extended periods of bad weather?
A: Yes. When designed with low average power consumption and sufficient battery capacity, the system continues operating through multiple cloudy days by prioritizing event-driven activity.
Q2: Is WiFi sufficient for outdoor PTZ surveillance compared with cellular solutions?
A: In locations with accessible local networks, WiFi offers stable performance without recurring data costs. Efficient encoding and local processing reduce dependence on constant high bandwidth.
Q3: Do PTZ functions significantly increase power consumption over time?
A: PTZ movement consumes more power momentarily, but modern systems activate motors only when needed. Overall consumption remains predictable within the solar energy budget.