Modern surveillance systems no longer rely on a single deployment logic. Wired and wireless architectures coexist across commercial facilities, residential estates, logistics centers, and temporary sites. The users’ buying decision is rarely about convenience alone, but reflects how to balance stability, network design, power planning, data integrity, and long-term maintenance.
Why does a connection type still shape the foundation of a security system?
Connection type defines how video data flows, how failures propagate, and how your system evolves. It not only affects installation speed but also determines fault tolerance, scalability, and lifecycle cost.
How does physical cabling influence signal reliability?
Wired cameras have an advantage when it comes to deterministic transmission. Wired Ethernet or fiber connections ensure consistent bandwidth, predictable latency, and high resistance to environmental noise. In a large installation, this reduces packet loss during peak recording windows and makes it easy to coordinate synchronized multi-camera footage.
Cabled connections also ensure that the data communication stream is isolated from the congestion of the home’s or business’s Wi-Fi networks. For instance, in an environment filled with industrial equipment or heavy metal-based structures, this segregation stops electromagnetic interference from interfering with video streaming and control signals.
How does wireless transmission change deployment logic?
The reliance of wireless cameras on shared spectrum brings rapid placement but introduces uncertainty, as signal strength fluctuates with distance, obstacles, and competing devices. When multiple cameras transmit simultaneously, routers become a performance bottleneck.
For sites with changing layouts or temporary monitoring needs, this trade-off is often acceptable. However, for fixed infrastructure, it requires careful network planning.
How should installation complexity affect your buying decision?
Infrastructure design often determines the total project duration more than the hardware cost.
Why do wired systems increase planning time?
Cable routing demands structural assessment, conduit planning, drilling, and power distribution design. In multi-floor buildings, compliance with fire codes and separation from high-voltage lines further extends preparation cycles.
However, once installed, wired networks rarely require re-engineering, and support predictable upgrades and stable long-term operation.
Why do wireless systems reduce early deployment friction?
Wireless cameras compress installation into three actions: power connection, app pairing, and positioning, enabling same-day deployment and relocation without civil work.
For pilot projects or rapidly changing sites, this simplicity accelerates decision cycles and lowers upfront labor risk.
How do bandwidth and compression change real-world performance?
Video quality depends less on resolution numbers than on how efficiently frames move across your network.
Why does a compression technology matter more than resolution?
In today’s codecs, the bitrate is lower while the details of the structural layout are retained, which allows more cameras to use the same uplink bandwidth without overloading the storage servers or the routers.
Meanwhile, great compression can enhance the accuracy of AI detection through the reduction of motion artifacts to produce fewer false alarms and clear evidence.
How does wireless traffic compete with other devices?
Wireless cameras share channels with phones, laptops, and IoT devices. When bandwidth collapses, frame drops appear before connection loss becomes visible.
In dense residential zones, interference becomes cumulative. Wired systems avoid this conflict entirely.
How does power supply determine long-term operational stability?
Power is the silent dependency of surveillance reliability.
Why are wired cameras less vulnerable to energy fluctuation?
Centralized power enables UPS integration and voltage regulation. Even short blackouts can be bridged without recording gaps. Stable voltage also protects PTZ motors and IR modules from premature failure.
Why do wireless cameras trade flexibility for energy management?
The operational model determines whether this flexibility outweighs additional upkeep. Wireless units often rely on adapters, batteries, or solar modules, so charging cycles, seasonal sunlight variation, and connector wear become maintenance variables.
How do intelligent features behave differently on wired and wireless platforms?
AI functions place new demands on hardware and networks.
How does edge processing reduce network pressure?
Local detection filters irrelevant frames before upload. Only meaningful events reach storage or cloud platforms, lowering bandwidth usage and speeding alerts.
How does wireless architecture affect real-time alerts?
Push notifications depend on uplink quality. When Wi-Fi degrades, alert latency increases, even if recording continues locally.
How should storage architecture influence camera selection?
Storage design governs evidence availability and compliance.
Why is local storage critical for unstable networks?
On-device cards protect data during outages, preventing evidence loss during router failure or ISP disruption.
How does cloud storage change compliance planning?
Cloud retention simplifies scaling but introduces jurisdiction and encryption policies. For regulated industries, hybrid models often dominate.
How can wireless product design reflect modern surveillance priorities?
Wireless hardware increasingly integrates functions once reserved for enterprise systems.
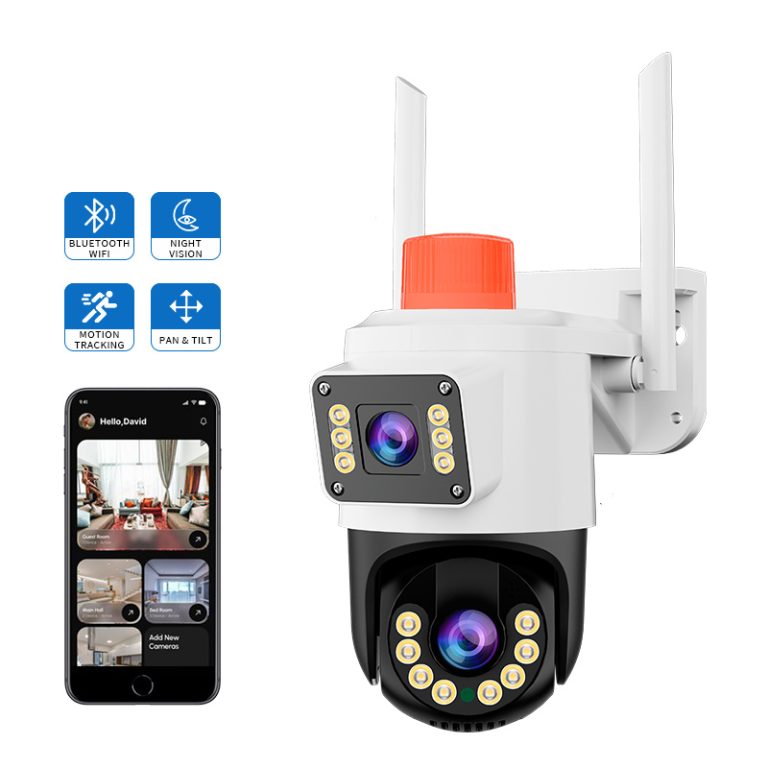
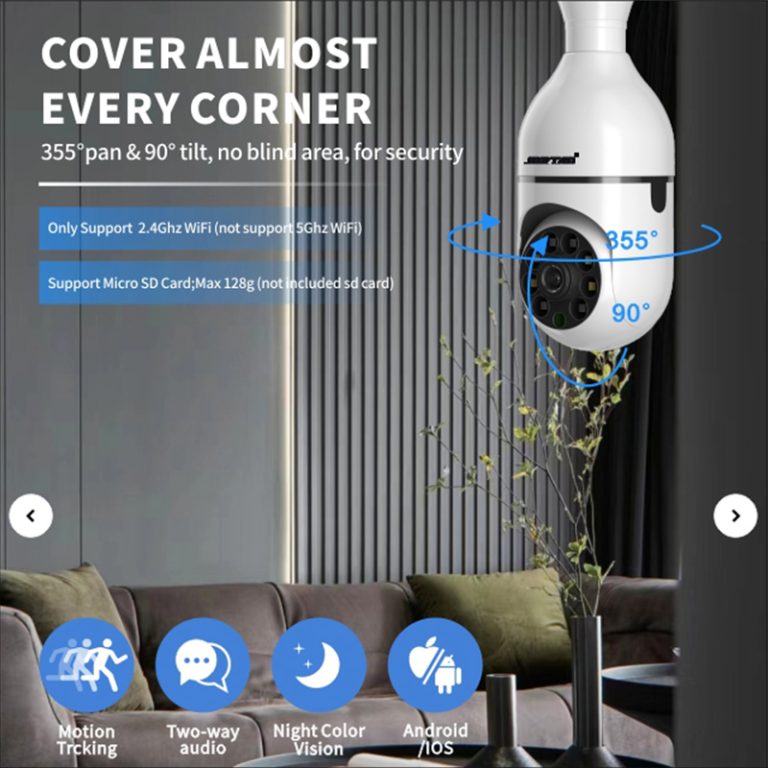
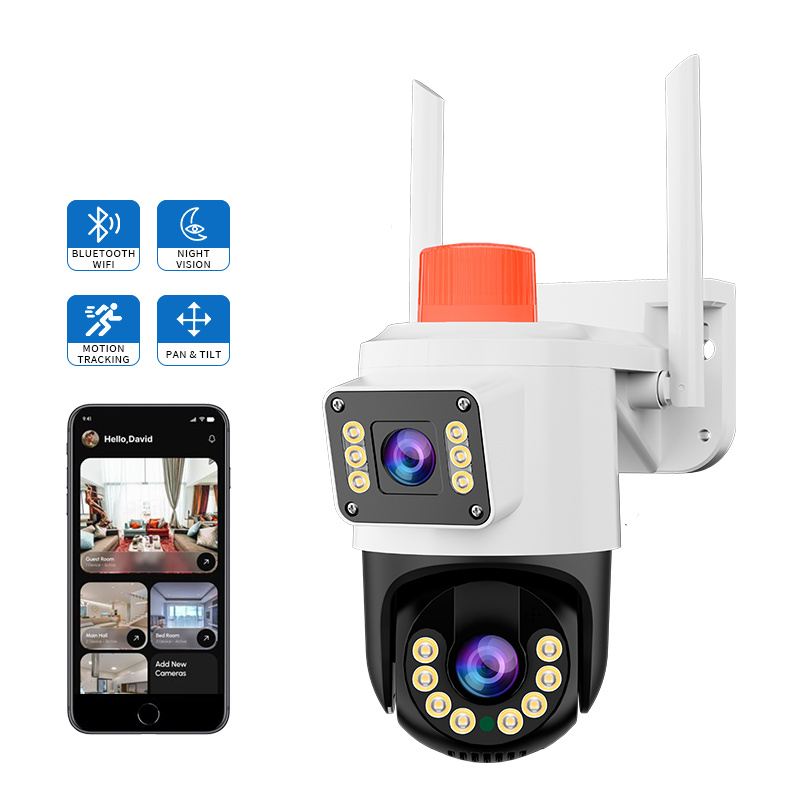
How does JT-9689UQJ support mobile-first surveillance workflows?
The JT-9689UQJ wireless IP camera integrates full-color night vision modes, AI-based human detection, local SD storage, and cloud synchronization into a compact form factor. Its design emphasizes remote operation through mobile platforms, enabling multi-user viewing, motion-triggered alerts, and secure rolling storage for continuous coverage. Such configurations illustrate how wireless cameras can deliver intelligent monitoring without dedicated network rooms or local servers.

Why does hardware interaction design affect system acceptance?
Usability drives long-term adoption as much as technical performance.
How does multi-user sharing reshape monitoring responsibility?
Modern systems distribute access across departments or family members. Permission-based sharing replaces centralized consoles, enabling parallel supervision without exposing configuration controls.
Why does a simplified configuration reduce lifecycle cost?
Three-step onboarding—power, app installation, pairing—lowers dependence on specialized technicians. Replacement units can be deployed without rewiring, so the downtime can be minimized.
How can other wireless models illustrate deployment diversity?
Different environments demand different design priorities.
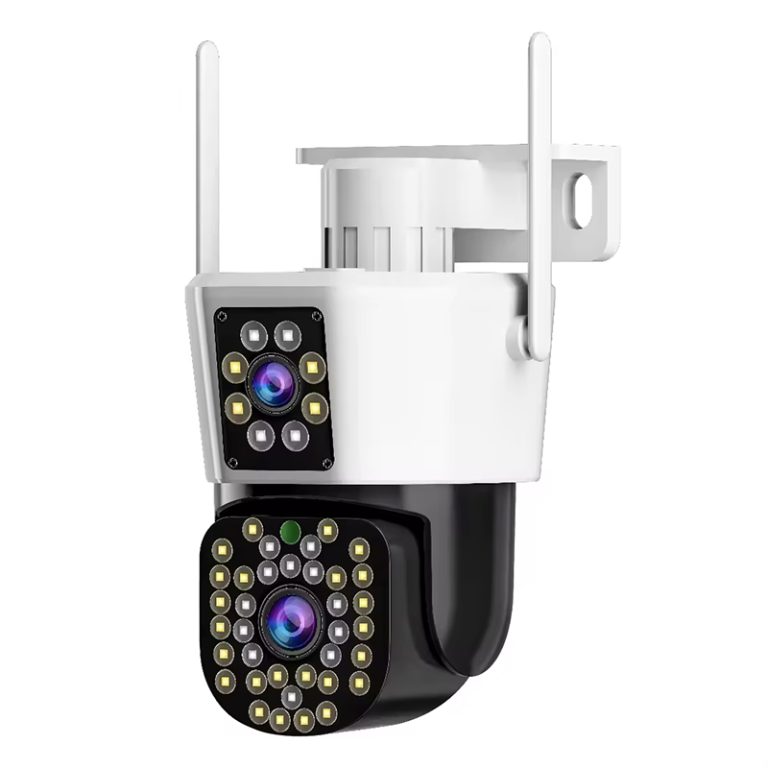
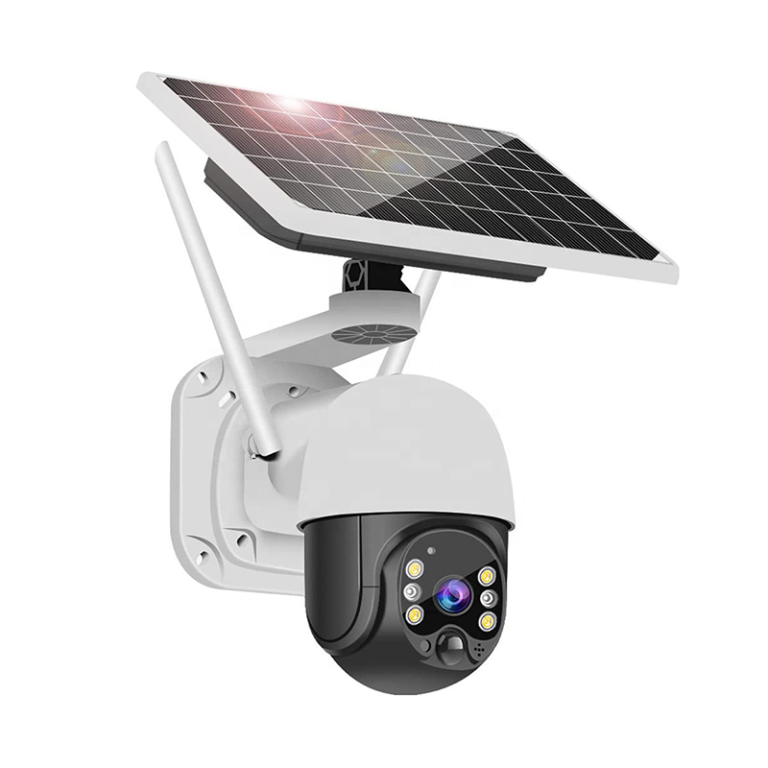
How does JT-8293QJ balance flexibility and performance?
The JT-8293QJ wireless IP camera demonstrates the advantage of access-point connectivity that allows monitoring in environments where external network connectivity fails. PTZ rotation, full-color modes, and platform access offer perimeter surveillance, storage, and mixed indoor-outdoor environments that lack cabling infrastructure.
How does manufacturer capability affect system reliability over time?
Hardware quality reflects the ecosystem behind it.
Why does production scale and system design experience matter?
Jortan integrates production, design, and technical service within a single manufacturing framework. Our company maintains facilities of over 30,000 square meters and develops monitoring equipment by using modern production lines and standardized quality assurance procedures. Our portfolio covers network cameras, lighting-integrated surveillance units, and intelligent monitoring devices designed for both consumer and commercial environments.
A long-term focus on process regularity, global manufacturing standards, and organized post-delivery networks helps to foster reliable firmware development and hardware compatibility through generations. It is our strong industrial base that helps reduce the chances of disruptions during system expansion or when component replacements are needed.
What common mistakes distort wired vs wireless comparisons?
Why does focusing only on installation speed mislead planning?
Fast deployment does not equal low cost. Maintenance cycles, firmware updates, and storage expansion often exceed initial hardware expense within two years.
Why does ignoring the environment cause failure?
RF noise, metal shielding, temperature extremes, and humidity directly affect wireless stability and sensor longevity. Site assessment prevents costly redeployment.
How should you evaluate total cost instead of device price?
How do network upgrades reshape hidden costs?
Routers, switches, and storage arrays frequently require upgrades after camera expansion, and these investments rarely appear in initial quotations.
How does maintenance frequency affect ROI?
Battery replacement, firmware testing, and periodic recalibration determine operational continuity more than purchase price.
FAQs
Q1: Is wireless surveillance reliable enough for commercial use?
A: Yes, when network design, storage redundancy, and environmental interference are properly evaluated. Reliability depends on architecture, not only the transmission method.
Q2: Do wired cameras always deliver better image quality?
A: No. Sensor quality, encoding efficiency, and night-vision design often influence usable footage more than cabling alone.
Q3: Should mixed wired and wireless deployments be avoided?
A: No. Hybrid systems are common and allow you to combine stability in fixed zones with flexibility in temporary or remote areas.