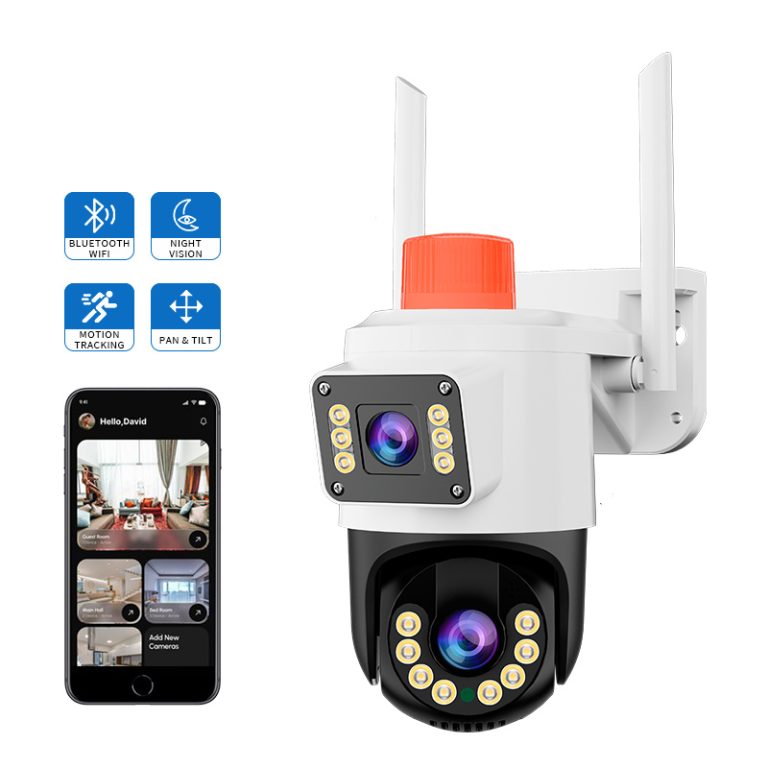
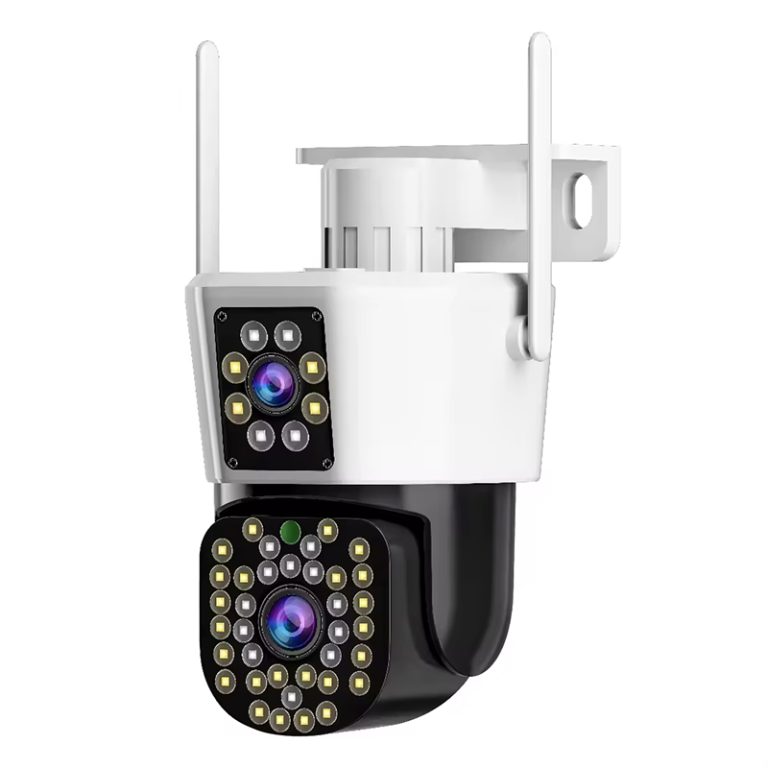
Wireless CCTV cameras with night vision are no longer optional accessories in modern security systems. Instead, they have become core infrastructure for residential properties, mixed-use buildings, small commercial sites, and perimeter monitoring. As surveillance systems evolve from recording tools into active risk-management assets, night performance and wireless reliability are now decisive factors rather than secondary features.
This article does not revisit basic camera concepts, but focuses on how you should evaluate wireless night-vision cameras when reliability, alert relevance, and long-term operational stability matter more than headline specifications. The discussion reflects current industry development trends, including AI-assisted detection, adaptive night imaging, and edge-based storage strategies.
What Real Security Risks Are You Trying to Control After Dark?
Before selecting any device, you need to clarify what types of incidents actually occur at night on your property. Night-time security risks are rarely uniform, and treating them as such often leads to ineffective coverage or excessive false alerts.
How different night-time risk patterns affect lens choice, illumination strategy, and alert logic
If your primary concern is unauthorized human entry, the system must prioritize subject separation and movement continuity rather than extreme night range. In contrast, vehicle-related monitoring places higher demands on dynamic range and illumination consistency. Static environments, such as a warehouse, require different night logic than residential entrances with frequent background motion.
Defining these patterns upfront allows you to avoid overbuilt night vision that looks impressive on paper but performs poorly in real conditions.
How Should You Evaluate Night Vision Quality Beyond “IR Distance” Numbers?
Quoted infrared distances often misrepresent actual night performance as they reflect illumination reach, instead of image usability.
Why infrared-only, white-light, and adaptive full-color night modes behave differently in actual deployments
Infrared night vision delivers consistent outlines but sacrifices color-based identification. White-light modes restore color but may introduce glare, attract attention, or increase power draw. Adaptive full-color strategies switch modes dynamically based on scene activity, offering a balance between discretion and clarity.
What matters most is how quickly the camera transitions between modes, how well it controls noise in low-light scenes, and whether color recovery improves recognition rather than simply brightening the image.
Does Wireless Connectivity Become a Risk Factor at Night?
Wireless transmission stability is often tested most severely at night, instead of during the day.
How Wi-Fi stability, encoding efficiency, and local fallback modes affect night surveillance continuity
Night-time activity spikes trigger higher bitrates, more frequent alerts, and greater upstream demand. Cameras that rely on inefficient encoding or unstable wireless links may drop frames or disconnect precisely when incidents occur.
Systems designed with modern compression and local recording buffers can maintain evidence continuity even during temporary network degradation. Local hotspot modes further reduce reliance on external connectivity when conditions are unpredictable.
Which Intelligent Functions Actually Reduce Night-Time Workload Instead of Adding Noise?
Not all intelligent features improve operational efficiency. Many increase alert volume without improving decision quality.
How human-focused detection and tracking logic improves night security accuracy
Human-centric detection algorithms filter environmental motion such as insects, rain, or shifting shadows. When combined with intelligent tracking, they preserve subject continuity even during PTZ movement or lighting changes.
At night, relevance matters more than sensitivity. A system that sends fewer but clearer alerts reduces response fatigue and improves overall situational awareness.
How Do You Balance Coverage Area and Detail Without Creating Blind Zones?
Night surveillance failures often stem from coverage design, rather than camera resolution.
Why PTZ behavior, rotation speed, and preset logic matter more at night than during the day
At night, excessive rotation can cause loss of context or missed transitions. Properly tuned PTZ logic emphasizes predictable patrol paths, sufficient dwell time, and smooth tracking rather than constant movement. This balance ensures that wide-area monitoring does not come at the cost of actionable detail.
Within this context, models such as the JT-8161QJ IP Security Camera are typically deployed where panoramic night coverage and adaptive illumination must work together without manual intervention.
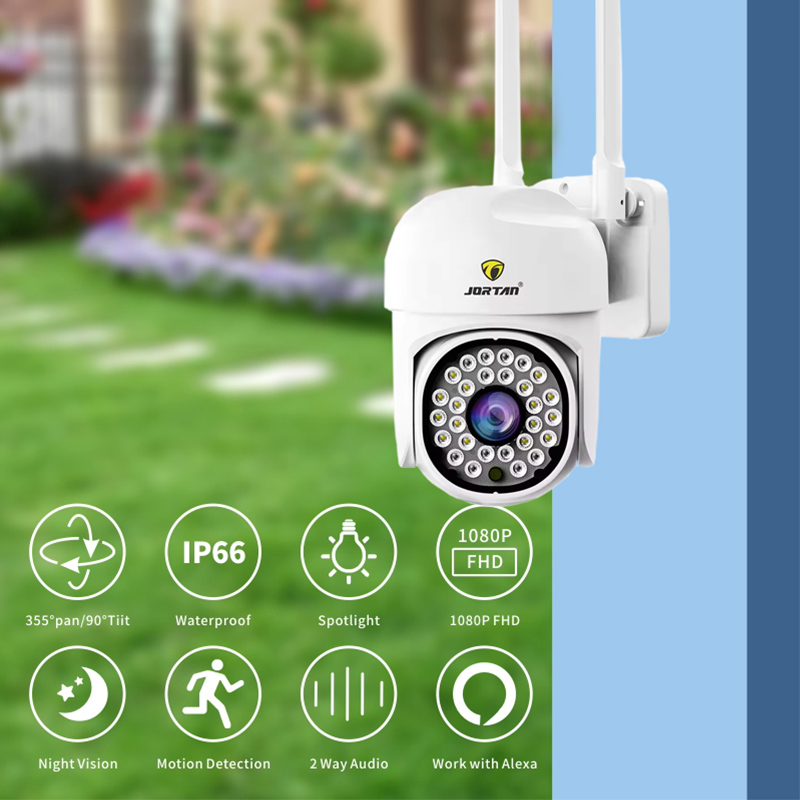

What Makes Installation and Long-Term Operation Reliable for Night Use?
Night performance degrades quickly if installation and power considerations are underestimated.
How enclosure rating, power stability, and environmental tolerance affect night imaging consistency
Illumination modules draw more power at night. Insufficient power margins often lead to reboot loops, reduced brightness, or unstable tracking, which weather exposure further worsen.
IP-rated enclosures, stable power delivery, and controlled installation angles preserve optical clarity and night-mode reliability over extended operating cycles.
In environments where wireless distance and physical exposure are both factors, solutions like the JT-8160QJ IP Security Camera are often selected for their balance between night imaging, enclosure protection, and wireless stability.

How Should Storage and Playback Be Evaluated for Night Incidents?
Night footage stresses storage systems differently than daytime video.
Why do night recordings stress storage systems differently than daytime footage?
Low-light scenes generate more noise, which increases storage demand and complicates compression. Effective systems apply noise reduction before encoding, preserving clarity while limiting storage growth.
Equally important is playback behavior. The ability to zoom, scrub, and review night footage without severe artifacting determines whether recorded evidence is actually usable.
Where Does Jortan Fit When You Need Reliable Night Surveillance Without Complexity?
After evaluating technical criteria, it is necessary to acquire a system that integrates them into a stable solution that is easy to deploy.
How Jortan structures wireless night-vision cameras around real deployment logic
Jortan approaches wireless night surveillance from a system perspective rather than a feature checklist. Our product emphasizes stable night imaging, adaptive illumination control, and efficient wireless transmission, supported by practical installation logic and local recording safeguards.
Instead of relying on excessive specifications, our focus is on consistent performance across real residential and light-commercial scenarios, particularly where night activity patterns vary, and network conditions are not always ideal. This positioning reflects broader industry shifts toward scenario-driven surveillance design rather than hardware-driven comparison.
Conclusion
Choosing a wireless CCTV camera with night vision is not a matter of selecting the highest numbers on a datasheet, but a system-level decision that must align night-time risk patterns, wireless reliability, intelligent detection behavior, and long-term operational stability. When these elements are evaluated together, night surveillance becomes a reliable security layer rather than a fragile technical add-on.
FAQs
Q: How much night-vision distance do you really need for most properties?
A: You should size night vision based on identification and reaction distance, not maximum illumination claims. Stable clarity within the actual activity zone is more valuable than an extreme range.
Q: Are full-color night cameras always better than infrared models?
A: Not necessarily. Full-color modes add value when ambient light or intelligent switching supports them. In low-activity zones, infrared or adaptive modes often deliver better consistency.
Q: Can wireless CCTV systems be trusted for night-time security?
A: Yes, if encoding efficiency, local storage, and wireless stability are matched to night traffic patterns and installation conditions.